Manufacturing Training Systems
Sort by
Learn about Manufacturing Training Systems
In this section you will learn more about Manufacturing Training Systems and different instructional tools, and how they are used to teach learners about smart manufacturing and industry 4.0 in an engaging hands on manner.
What are Manufacturing Training Systems?
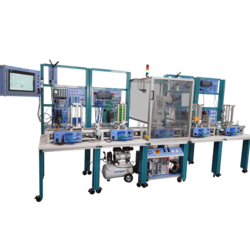
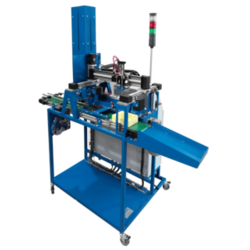
Manufacturing training systems are educational tools and platforms designed to provide hands-on experience and theoretical knowledge about manufacturing processes and technologies. These systems are used to train students, technicians, and engineers in various aspects of manufacturing, including automation, robotics, machining, and quality control. They simulate real-world manufacturing environments, allowing trainees to develop the necessary skills to operate and maintain manufacturing equipment, understand production workflows, and implement modern manufacturing techniques.
What Type of Manufacturing Training Systems Exist?
There are various types of manufacturing training systems, each tailored to different aspects of manufacturing. Some common types include:
-
Automation and Robotics Training Systems:
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) Trainers: These systems simulate industrial automation processes, helping trainees understand how to program and troubleshoot PLCs used in automated manufacturing.
- Robotic Arm Trainers: These provide hands-on experience with industrial robots, teaching programming, operation, and maintenance.
- CNC Machine Training Systems: Simulate the operation of computer numerical control machines, allowing users to practice programming and machining tasks.
-
Mechatronics and Integrated Systems Training:
- Mechatronics Trainers: Combine mechanical, electrical, and computer systems, teaching how to design and operate integrated manufacturing systems.
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Trainers: These systems teach the principles and applications of fluid power systems used in industrial automation.
-
Quality Control and Inspection Systems:
- Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) Trainers: Provide training in precision measurement and quality control techniques, critical in manufacturing environments where accuracy is essential.
- Vision Inspection Systems: Teach how to use machine vision for automated quality control and defect detection.
-
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) Training Systems:
- 3D Printers: Used to train on the design, setup, and operation of additive manufacturing technologies, focusing on material properties and printing techniques.
-
Lean Manufacturing and Process Simulation:
- Lean Manufacturing Simulators: These training tools help learners understand lean principles, waste reduction, and process improvement in a simulated manufacturing environment.
- Process Flow Simulators: Used to teach the optimization of manufacturing processes, including workflow analysis and bottleneck identification.
-
Virtual and Augmented Reality Training:
- VR/AR Training Modules: Provide immersive environments for training in complex manufacturing tasks, enhancing learning through realistic simulations without the need for physical equipment.
Why Use Manufacturing Training Systems?
Manufacturing training systems are essential for several reasons:
-
Skill Development: These systems provide practical, hands-on experience that is crucial for developing the technical skills needed in modern manufacturing environments.
-
Workforce Readiness: They prepare students and employees for the demands of the manufacturing industry, ensuring they are competent in operating advanced machinery and systems.
-
Safety and Efficiency: By simulating real-world scenarios, these systems allow trainees to learn in a safe environment, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall operational efficiency.
-
Adapting to Technological Advances: Manufacturing is constantly evolving with new technologies. Training systems help workers stay up-to-date with the latest advancements, such as automation, robotics, and smart manufacturing.
-
Cost-Effective Training: These systems provide a controlled environment where mistakes can be corrected without the costly consequences of errors on a real production line.
-
Standardization of Training: They help ensure consistent training across different facilities and institutions, leading to a more uniform skill set among workers.
Best Practices for Using Manufacturing Training Systems
To maximize the benefits of manufacturing training systems, it's important to follow best practices:
-
Comprehensive Curriculum Integration: Align training systems with a well-structured curriculum that covers both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Ensure that the training is relevant to current industry standards and technologies.
-
Regular Updates and Maintenance: Keep the training systems up-to-date with the latest software, hardware, and manufacturing practices. Regular maintenance ensures the equipment functions correctly and reflects current industry practices.
-
Hands-On Learning: Encourage active, hands-on participation in training sessions. Practical experience is crucial in developing the skills needed for effective manufacturing operations.
-
Safety First: Incorporate safety training as a core component of the curriculum. Ensure that users are aware of potential hazards and the proper safety protocols when using training equipment.
-
Feedback and Assessment: Implement regular assessments to gauge trainees' understanding and skills. Provide constructive feedback to help learners improve and understand areas where they need more focus.
-
Industry Collaboration: Collaborate with industry partners to ensure that training programs meet the needs of employers and are aligned with real-world manufacturing practices.
-
Customizable Training Modules: Offer flexible training modules that can be tailored to the specific needs of different learners, whether they are novices or experienced professionals.
By following these best practices, institutions and companies can effectively use manufacturing training systems to build a skilled, competent, and safety-conscious workforce, ready to meet the demands of modern manufacturing.