Industrial Maintenance Training Equipment
Sort by
Learn more about Industrial Maintenance Training Equipment
In the below section we will cover a few topics regarding didactic equipment and training systems for teaching industrial maintenance skills.
What is Industrial Maintenance?
Any industry which uses some type of machinery, equipment or infrastructure installments have the need to continuously maintain, repair and replace these vital assets.
Examples of such industries are consumable goods manufacturing (such as textiles, cosmetics, electronics etc.) and the durable goods manufacturing (such as automotive, aerospace, defense etc.), processing industry (such as food & pharmaceutical, pulp & paper) extractive industries (such as oil & gas, mining etc.) transportation services (shipping, aviation, trucking etc.) and infrastructure (road & rail, built environment etc.).
Depending on which type of industry the future maintenance technician will work in, necessary skills can range across various topics such as plumbing system maintenance, piping system maintenance, industrial rigging principles, forklift safety, industrial electrical skills, building maintenance, lubricator training, mechanical systems, HVAC-R maintenance, welding training, instrumentation and control systems, DC equipment and controls, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), AC control equipment, hydraulics, pneumatics, industrial robotics and much more.
Best practices teaching Industrial Maintenance
Most workplace accidents happen by improper usage of machines and equipment, which is why it is vital to train future technicians in a hands-on manner where they get access to, and experience with industrial technologies.
There are various benefits of training students with hands-on training systems, such as: increased safety due to early familiarity with health & safety processes, increased content retainment by learning both theoretically and practically, increase student engagement due to ownership of own learning experience, increased critical thinking when focus is on troubleshooting and problem solving rather than memorizing information for an exam, better workplace preparedness due to mentoring by skilled trainers and educators with real world experience.
Since industrial maintenance is also becoming increasingly seen as a service profession, employers look for skills that traditionally have been labeled “soft-skills” but more often these days are referred to as “employability skills” such as communication, leadership, collaboration, continuous learning, motivation and initiative, adaptability etc.
Types of Industrial Maintenance Training Equipment
There are many different types of industrial maintenance training equipment and teaching systems which are normally used in classrooms, workshops, and training centers, a few examples below:
- Electrical trouble shooting training stations
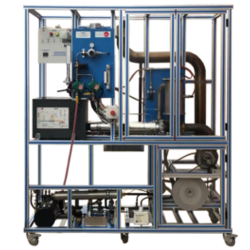
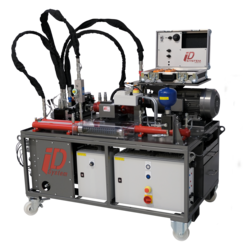
- Mechanical training stations / Industrial pumps
- Fluid Power (Hydraulics & Pneumatics)
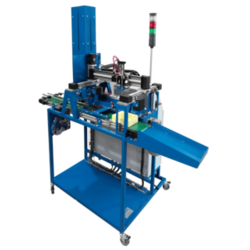
- Mechatronics Training Systems
- Industrial Robotics
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
- Industrial Process Controls