Mechatronics Lab Equipment & Training Systems
Sort by
Learn more about Mechatronics Lab Equipment
In this section you will learn about what Mechatronics is, what a mechatronics specialist does, where he or she works and what can be expected from the future job market. Furthermore, we will cover the best practices for teaching mechatronics, the different types of mechatronics lab equipment and how to think about equipping your own mechatronics laboratory or training center.
What is Mechatronics?
Mechatronics is a multidisciplinary branch focusing on mechanical and electrical engineering, and involves robotics, control systems, electro-mechanical systems etc.
A mechatronics specialists workplace ranges from academia, laboratories, manufacturing, or processing plants, to engineering design offices.
With the growth of industrial automation all major production industries need mechatronics specialists: food & pharma, chemicals, processing, consumable goods, textiles, electronics, durable goods, automotive, aerospace, defense etc.
Mechatronics specialists are involved with design, development, manufacturing and maintenance of advanced engineering systems and smart products, as well as automation of industrial tasks.
Why should we teach mechatronics?
Industrial automation and mechatronics do not only touch upon but have profound impact on the competitiveness of companies and entire industries.
To answer the needs for smart factories and Industry 4.0, the last decade Mechatronics has become one of the fastest growing technical education programs globally.
Various reports show that the profession has a great future. The number of jobs for mechatronics specialists are experiencing a moderate growth and salary expectations are good.
Best practices for teaching Mechatronics
Electronics are becoming a natural part of all kinds of physical mechanical products, so combining mechanical engineering with electrical engineering is becoming a more and more important aspect.
Everything will be connected to the internet and it will make production faster, easier, more flexible and can help companies to customize production according to their client’s needs.
We now have an innovation economy and when students join the workforce they are expected to work in small cross disciplinary teams, how does that impact the best way for teaching Mechatronics?
- Larger companies are typically looking for students with very specialized knowledge and skills, while startups and SMEs are rather looking for those multiskilled team members.
- There seems to be a divide across educational institutions as whether to integrate mechatronics into other subjects, or whether to teach mechatronics as a separate classes and programs.
- Another question is how do embed cross disciplinary competences such as project management, leadership, and communication into the mechatronics education.
Irrespective of which approaches, methodologies and technologies are used everyone seems to be agreeing on one important point: it is extremely important to combine theory with practice.
Types of Mechatronics Training Equipment
Mechatronics training equipment comes in many shapes and sizes, below we have summarized a few different types.
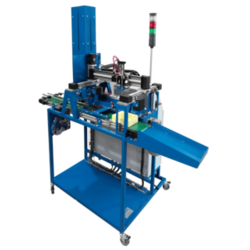
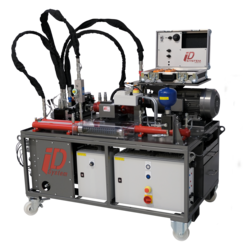
Technical Training Equipment
Mechatronics is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering covering various subfields which each can be learnt separately in a hands-on manner. For example, you can find training equipment for hydraulics, pneumatics, PLC training rigs, process control, or industrial robotics.
Desktop Mechatronics Equipment
There exist simpler types of mechatronics training equipment that are laid out on a tabletop. These systems are smaller and can often be packed up and stored away when not in use, which makes them suitable for a foundational training in mechatronics.
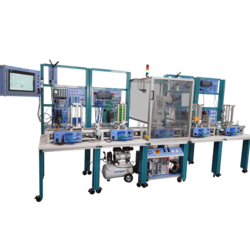
Modular Production Systems / Flexible Manufacturing Systems
These types of training systems are always put together to resemble a production line through which a “product” is moved between different workstations to add value. Typically, each workstation is commanded by a PLC and can be used either individually or combined with other workstations.
Learning Factories
Learning factories are the top notch of mechatronics training equipment. These training solutions are normally semi purpose built and designed to include much more than a modular production system. According to Abele E. (2016), a Learning Factory in a narrow sense is a learning environment specified by:
- processes that are authentic, include multiple stations, and comprise technical as well as organizational aspects,
- a setting that is changeable, and reassembles a real value chain,
- a physical product is being manufactured, and
- a didactical concept that comprises formal, informal, and non-formal learning, enabled by own actions by the trainees, in an on-site learning approach.